Rail track monitoring – follow your track geometry and defects remotely and in real time with our IoT solution
Railway tracks are permanently subject to numerous constraints, which can be weather conditions (thermal amplitude depending on the season, etc.), the stability of the ground (natural movements, seismic activity, etc.) or wear and tear linked to their use (passage of trains, etc.). Playing a key role in reducing carbon gases in transport, and driven by the will and ambition of the public authorities, the railway network must also be able to manage increasing demands for capacity and availability (both for passengers and freight).
The monitoring of rail defects is therefore a major challenge for both infrastructure managers and network operators. It is in fact a question of guaranteeing smooth running on the track, not only for passenger comfort but also – and above all! – for safety reasons.
A challenge: to overcome the incompatible triangle of “cost – exhaustiveness – immediacy”
Currently, this rail track geometry monitoring is mainly carried out by inspection rounds, which can be visual and/or done with instruments. These rounds are costly, both in terms of time and equipment, especially as it is sometimes necessary to immobilize all or part of the rail traffic.
Detecting defects is therefore limited – firstly, because the prohibitive cost of the rounds means that only certain portions of track are inspected daily (with no direct logic between the monitoring and potential defects); secondly, because it is not possible to follow up on the apparition or the development of the deterioration of the defects observed between two inspections.
An idea: take advantage of ordinary journeys to observe and evaluate first-hand the state of the network
This solution takes the aforesaid difficulties into account and puts forward a very simple idea – capitalize on the ordinary rotations of the rolling stock to make it a first-hand witness of the state of the network.
We have therefore developed an end-to-end IoT solution based on:
- Non-intrusive instrumentation of part of the rolling stock. This involves equipping several “control” trains with our Railnode IoT sensors. Two would be positioned on a bogie (accelerometers) and one placed on the roof of the rolling stock (GPS terminal).
- Instrumentation, at certain points along the track, with Bluetooth IoT sensors to ensure continuity of GPS tracking in underground zones.
- The development of algorithms enabling:
- The precise geolocation of potential defects (not all shocks are defects but all defects generate shocks).
- The creation of baselines for each defect and the anticipation of their development.
- Characterization – taking into account the context – of the different types of defects.
4. Transformation of the data into information available via the Oxygen platform.
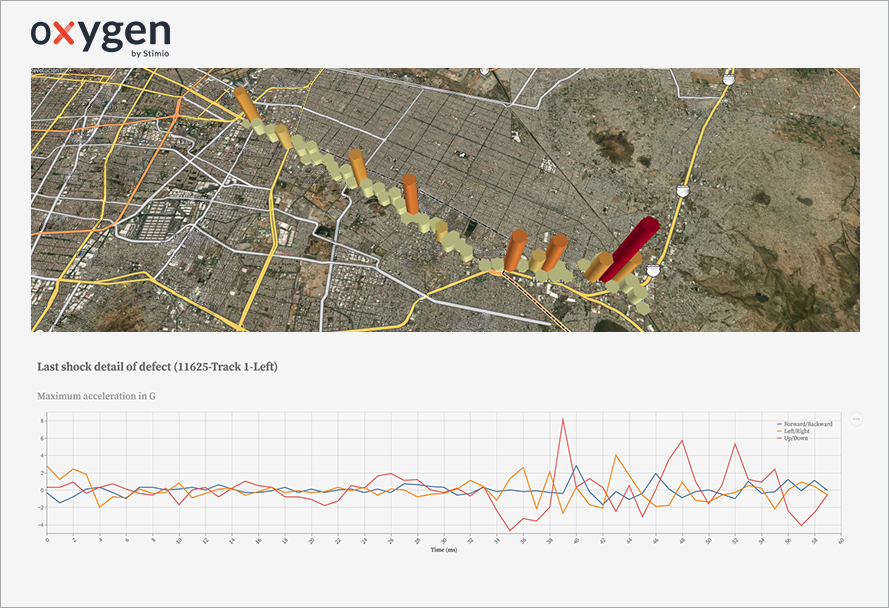
A tool: to monitor in real time the position and characteristics of defects on the track
Our tool enables us to deliver immediate, clear and reliable information on network defects and in particular :
– Their location
– Their main characteristics
– Their development over time
– Anticipation of their potential deterioration
– Details of the shocks they have generated
In addition to data visualization, it is a tool which can really help in decision-making and can lead to maintenance prescriptions, particularly in the prioritization of the segments on which to intervene.
Focus on data science / engineering:
The central idea of the work on data is the transformation of a series of “observations” (sensor telemetry) into relevant information that can be used directly by the operational teams.
From simple GPS positions, it is possible, for example, to reconstruct itineraries, calculate speeds, etc., or even estimate the types of difficulties that a train may have encountered on its journey.
The observation of accelerations – which are nothing more than a series of points distributed along three axes, vertical, horizontal and lateral – then takes on its full meaning. It becomes possible, not only to locate the shock that they show (by correlating the GPS “timestamp” with the accelerometer “timestamp”), but also to specify the context and/or eliminate certain interpretations. For example, a certain frequency could be explained not by the shock itself, but by the speed of the train.
Our rail defects monitoring solution is therefore taking on the challenge of using data. By implementing reliable sensors (“on-board development”), the industrial management of data input and output (“data engineering”) and the enhancement of the latter (“data science”), it is possible to achieve the three objectives: exhaustiveness, immediacy and controlled cost.
A wide portfolio of railway-certified connected devices
Stimio offers a portfolio of connected devices for the railway industry, covering a wide range of use cases to help operators face their many challenges. In addition to supervision of the evolution of track geometry, Stimio’s solutions are designed to monitor:
- Monitoring and prediction of catenary tensioning;
- Remote surveillance of rail temperature;
- Pantograph health and lifting function;
- Monitoring and prediction of sand levels in silos.
Stimio’s end-to-end IoT solutions are already implemented in more than 30 use cases in the railway industry, for rolling stock remote condition monitoring, wayside and signaling concerns.
To learn more
Railnode
Railnode is Stimio's certified rail solution for collecting data and delivering them to Oxygen and business information systems.
Learn more →
Oxygen Asset Management
From device management to visualisation and prediction, Oxygen Asset Management unlocks data’s potential and turn them into intelligent and actionable information.
Lean more →
Let's talk about your concerns
Related news
Remote and real-time flood monitoring of transformers
January, 28th, 2021Flood remote monitoring of transformersIn 2016, violent floods hit French territory. Following this episode, ENEDIS, the distribution managing company of the French electricity network (38,000 employees, 37 million customers, 14 billion € of...
Remote condition monitoring of train doors
November, 17th, 2020Train door condition monitoringRolling stock operators manage heterogenous rolling stock fleets composed of recent and old vehicles. Older trains are less “connected” and therefore provide less monitoring data related to system status and health....
Remote monitoring of transport conditions
November, 20th, 2020Remote monitoring of transport conditions Stimio relied on its product offering to provide an end-to-end solution allowing its customer, an independant supply-chain provider specialised in sensitive high-value asset transportation, to remotely...




